The Latest Advances in Hernia Repair Surgery: What's New in 2024?
Wednesday, 15th May 2024Hernia repair is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures worldwide, and the field has seen significant advancements in recent years. As we move through 2024, new technologies, techniques, and materials continue to improve the outcomes and recovery times for patients undergoing hernia repair. Here’s a look at some of the latest developments in this area.
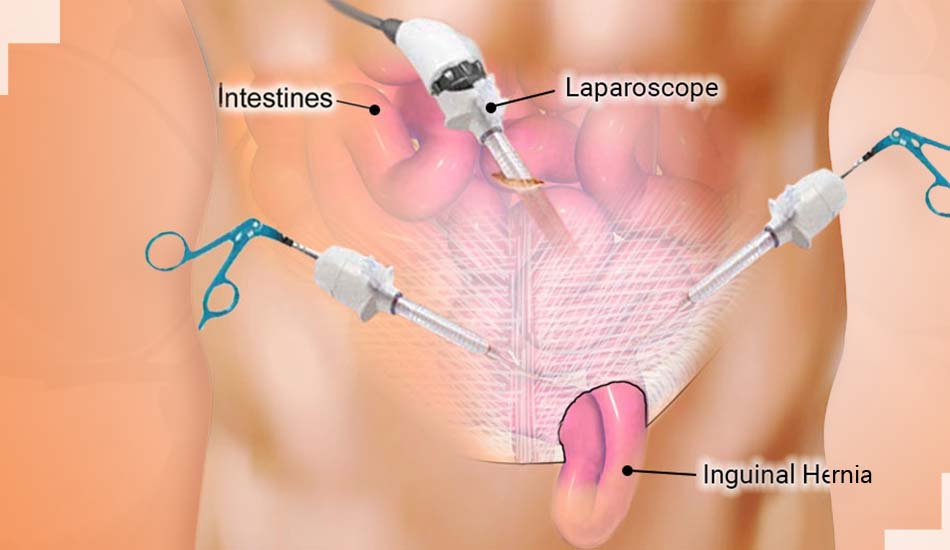
Robot-Assisted Hernia Repair
Robot-assisted surgery has been gaining traction across various surgical disciplines, and hernia repair is no exception. In 2024, these systems have become even more advanced, offering surgeons unprecedented precision and control. This technology allows for smaller incisions, which can lead to reduced pain and quicker recovery times for patients. Additionally, the enhanced visualization and increased range of motion with robotic tools help surgeons perform more complex repairs with greater accuracy.
Absorbable Synthetic Meshes
The use of surgical mesh is a standard practice in hernia repairs to provide additional support to the weakened area. Recent advances have introduced new types of synthetic meshes that are absorbable. These materials are designed to provide temporary reinforcement while promoting new tissue growth, after which they gradually dissolve, minimizing long-term complications associated with non-absorbable meshes, such as infections or mesh rejection.
Pain Management Innovations
Post-operative pain management is crucial in hernia surgery recovery. In 2024, there are new approaches being utilized to minimize discomfort and reduce the reliance on opioids for pain relief. These include the use of long-acting local anesthetics and non-narcotic pain relief options that are administered during surgery to provide pain control for up to 72 hours post-operation. This not only improves comfort but also accelerates recovery by enabling patients to move and return to normal activities sooner.
Enhanced Recovery Protocols
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols have been refined in 2024 to include specific guidelines for hernia repair patients. These protocols focus on reducing the stress of surgery, optimizing pain management, and expediting the return to normal activities. Key components include pre-operative nutrition, minimizing fasting, optimizing fluid management during surgery, and early mobilization after surgery. Hospitals adopting these protocols have reported shorter hospital stays and lower complication rates.
3D Imaging and Customization
Advances in 3D imaging have enabled more precise pre-operative planning. Surgeons can now create a detailed 3D model of the patient’s anatomy, allowing them to tailor the surgical approach to each individual’s specific needs. This is particularly useful in complex or recurrent hernia cases where precision is paramount. Furthermore, 2024 has seen the growth of custom-made meshes, shaped and sized based on individual patient scans, ensuring a perfect fit and potentially reducing the risk of recurrence.
Biological Meshes
Biological meshes, made from human or animal tissue, have been further developed to improve compatibility and reduce the body’s inflammatory response. These meshes are treated to remove cellular material that can lead to rejection, leaving behind a structure that supports the patient’s tissue growth. Recent studies have shown promising results in reducing the rate of hernia recurrence and minimizing the risk of complications associated with synthetic meshes.
Conclusion
The field of hernia repair surgery is rapidly evolving, with 2024 bringing multiple advancements that offer significant benefits to patients. These innovations aim to reduce recovery times, minimize pain, lower recurrence rates, and ultimately, improve the quality of life for those undergoing hernia repair. As these technologies and techniques continue to develop, they promise even better outcomes for future patients.



