Enlarged Prostate Explained: Why It Happens and How to Prevent It
Thursday, 30th May 2024An enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition in older men that can cause urinary problems and affect quality of life. Understanding why it happens and how to prevent it can help manage symptoms and maintain prostate health. This article explores the causes of an enlarged prostate and offers practical tips for prevention.
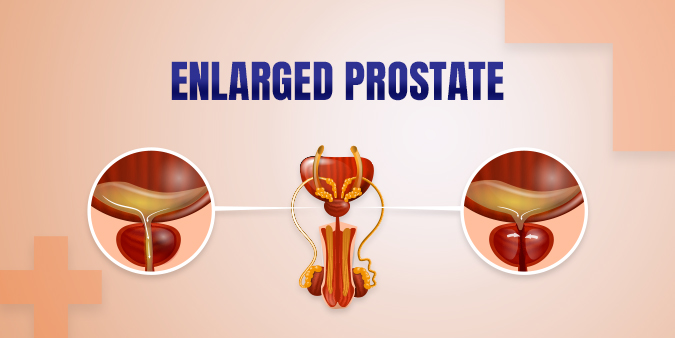
What is an Enlarged Prostate?
The prostate gland is a small, walnut-sized organ located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. An enlarged prostate occurs when the gland grows larger, potentially squeezing the urethra and causing urinary symptoms.
Why Does the Prostate Enlarge?
Aging
Aging is the most significant factor in prostate enlargement. As men age, hormonal changes, particularly an increase in dihydrotestosterone (DHT), can stimulate prostate growth. BPH is rare in men under 40 but becomes more common with advancing age, affecting about 50% of men in their 50s and up to 90% of men in their 80s.
Hormonal Changes
Changes in hormone levels play a crucial role in prostate growth. The balance between testosterone, estrogen, and DHT changes as men age. Higher levels of DHT in the prostate can lead to cell growth and enlargement.
Genetics
Genetics can influence the likelihood of developing BPH. Men with a family history of prostate problems are more likely to experience prostate enlargement.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle factors can contribute to an enlarged prostate, including:
- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, can increase the risk of BPH.
- Lack of Exercise: A sedentary lifestyle is associated with a higher risk of prostate enlargement.
- Diet: A diet high in red meat, processed foods, and dairy products may contribute to prostate growth.
Symptoms of an Enlarged Prostate
An enlarged prostate can cause a range of urinary symptoms, including:
- Frequent urination: Needing to urinate more often, especially at night (nocturia).
- Urgency: A sudden, strong urge to urinate.
- Weak urine stream: Difficulty starting urination or a stream that stops and starts.
- Incomplete emptying: Feeling that the bladder is not completely empty after urinating.
- Dribbling: Leakage of urine after finishing.
How to Prevent Prostate Enlargement
While aging and genetics cannot be controlled, certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of prostate enlargement and manage symptoms.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of BPH. Regular physical activity and a balanced diet can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise helps improve overall health and can reduce the risk of BPH. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are beneficial.
Eat a Prostate-Friendly Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in prostate health. Consider the following dietary tips:
- Increase fruits and vegetables: These are high in antioxidants and can help reduce inflammation.
- Include healthy fats: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts are beneficial.
- Limit red meat and processed foods: These can contribute to inflammation and hormone imbalances.
- Consume more soy products: Foods like tofu and soy milk contain compounds that may help regulate hormone levels.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential for overall health, including prostate health. However, avoid excessive fluid intake before bedtime to reduce nighttime urination.
Limit Caffeine and Alcohol
Limiting caffeine and alcohol can help manage urinary symptoms. Both substances can irritate the bladder and increase the frequency and urgency of urination.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking can contribute to many health problems, including an increased risk of BPH. Quitting smoking can improve overall health and reduce the risk of prostate issues.
Manage Stress
Managing stress is important for overall well-being. Chronic stress can impact hormone levels and contribute to prostate enlargement. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress.
Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help monitor prostate health and detect any issues early. Discuss any urinary symptoms or concerns with your doctor.
Conclusion
An enlarged prostate is a common condition that can impact quality of life, but understanding its causes and taking preventive measures can help manage symptoms and maintain prostate health. By maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, eating a balanced diet, and managing stress, you can reduce the risk of BPH. Regular medical check-ups are also crucial for early detection and effective management of prostate issues. If you experience symptoms of an enlarged prostate, consult with your healthcare provider to discuss appropriate prevention and treatment strategies.



