Ear Drum Repair Made Easy: Understanding Tympanoplasty
Wednesday, 22nd May 2024Tympanoplasty, a surgical procedure to repair a damaged eardrum, can significantly improve hearing and quality of life. This article will help you understand what tympanoplasty involves, how to prepare for it, and what to expect during recovery.
Introduction to Tympanoplasty
Tympanoplasty is a surgical intervention designed to repair a perforated eardrum, enhancing hearing and preventing recurring infections. With advancements in medical technology, this procedure has become relatively straightforward and effective.
The Role of the Eardrum
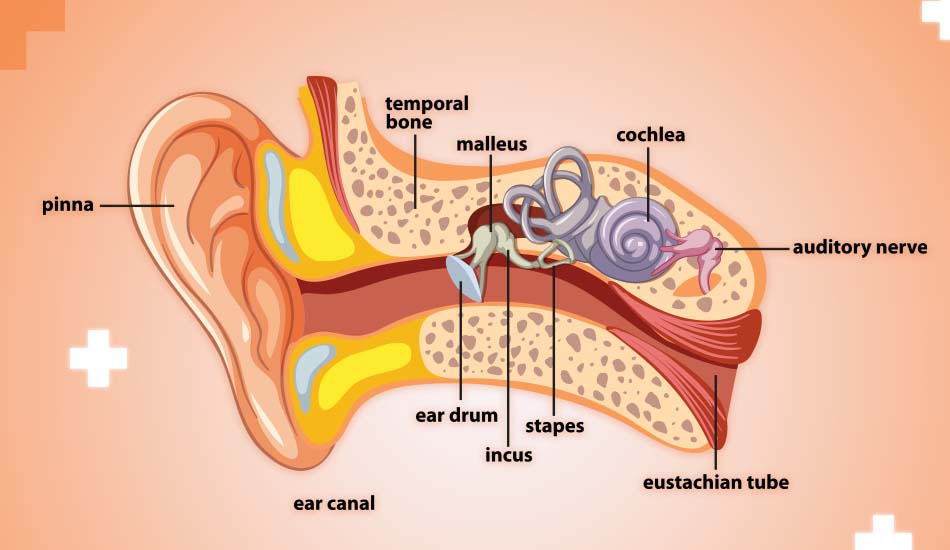
The eardrum, or tympanic membrane, is a thin tissue that separates the outer ear from the middle ear. It vibrates in response to sound waves, which then get transmitted to the inner ear, playing a crucial role in hearing.
Causes of Eardrum Damage
Eardrum damage can occur due to:
- Chronic ear infections
- Traumatic injuries
- Sudden loud noises
- Insertion of foreign objects into the ear
Why Tympanoplasty is Needed
Tympanoplasty is necessary when:
- There is a perforation or hole in the eardrum.
- Chronic ear infections are present.
- Hearing loss affects daily life.
Types of Tympanoplasty
1. Type I Tympanoplasty (Myringoplasty)
Repairs a simple perforation of the eardrum.
2. Type II Tympanoplasty
Involves repairing the eardrum and the malleus bone.
3. Type III Tympanoplasty
Repairs the eardrum and the incus bone.
4. Type IV Tympanoplasty
Reconstructs the eardrum and the stapes bone.
Preparing for Tympanoplasty
Before the surgery:
- Discuss your medical history with your doctor.
- Follow pre-surgery instructions, such as fasting.
- Arrange for post-surgery transportation and care.
The Tympanoplasty Procedure
The procedure typically involves:
- Administering anesthesia.
- Making an incision behind the ear to access the eardrum.
- Using a graft to repair the eardrum.
- Closing the incision with stitches.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Post-surgery care includes:
- Resting and avoiding strenuous activities.
- Keeping the ear dry and clean.
- Taking prescribed medications to manage pain and prevent infection.
Long-Term Recovery Tips
For a smooth recovery:
- Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
- Avoid blowing your nose forcefully.
- Refrain from flying or diving until fully healed.
- Attend all follow-up appointments.
Potential Risks and Complications
Risks include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Temporary dizziness or hearing loss
- Tinnitus
- Graft failure
Hearing Improvement After Tympanoplasty
Most patients experience significant hearing improvement post-surgery. Full benefits are typically realized within a few weeks as swelling subsides and healing progresses.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Ear Health
To maintain ear health and prevent future issues:
- Avoid inserting objects into your ears.
- Protect your ears from loud noises.
- Maintain good ear hygiene.
- Stay hydrated and follow a balanced diet.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Contact your doctor if you experience:
- Severe pain or swelling
- Persistent dizziness or nausea
- Discharge or bleeding from the ear
- Signs of infection, such as fever
Conclusion
Tympanoplasty offers a viable solution for repairing a damaged eardrum, leading to improved hearing and a better quality of life. Understanding the procedure and following recovery tips can ensure a successful outcome.



